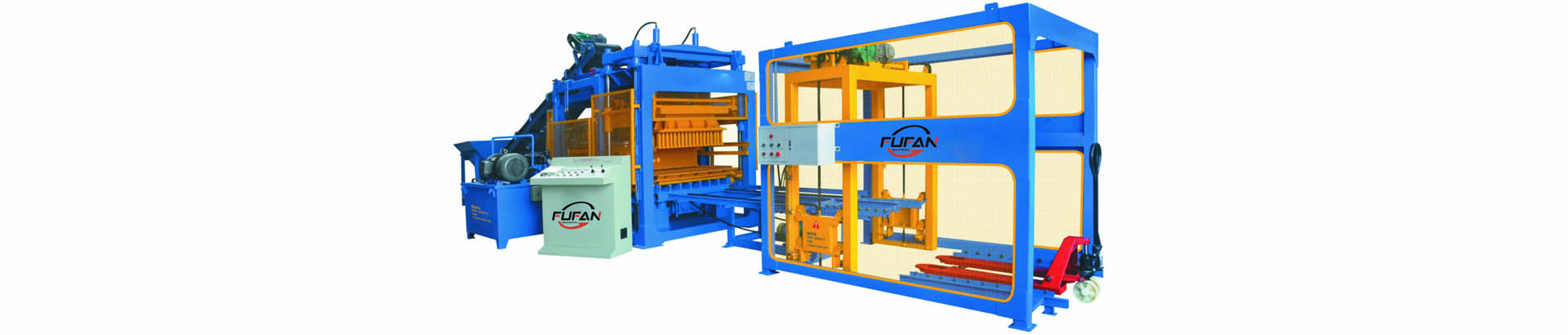
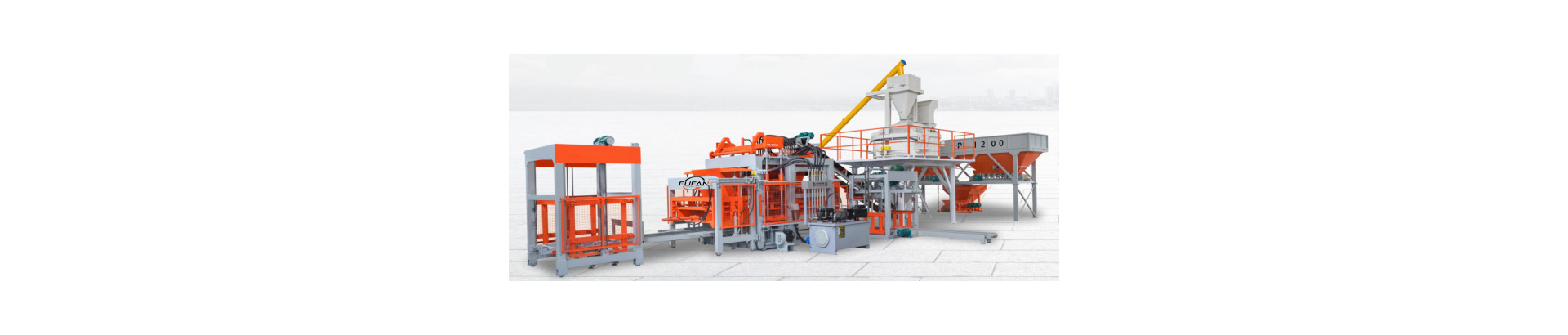
Fly ash bricks are made of fly ash, sand, lime, and gypsum. The ingredients are combined, the mixture is pressed into moulds, and the bricks are heated in a kiln to cure them. Due to their waste materials use and lower energy requirements during production, fly ash bricks are an environmentally beneficial substitute for conventional clay bricks.
Bricks have been a popular building material for centuries due to their versatility, durability, and ease of use. However, the brick manufacturing process has evolved, with new technologies and materials being introduced to improve their quality and sustainability. One such innovation is the production of fly ash bricks made from fly ash, a by-product of coal-fired power plants. By utilising fly ash, the manufacturing process of fly-ash bricks offers an eco-friendly solution to waste disposal. We will also examine the advantages and disadvantages of fly ash bricks compared to traditional clay bricks. Fly ash bricks have become increasingly popular in the construction industry as they offer a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to traditional clay bricks. Therefore, understanding the manufacturing process of fly ash bricks is crucial for anyone involved in the construction industry or interested in eco-friendly building materials.
Did you know? Fly ash bricks have better thermal insulation properties than traditional clay bricks. This helps buildings cooler in hot weather and warmer in cold weather, resulting in significant energy savings.
What are Fly Ash Bricks?
Fly ash, cement, sand, and water are combined to create fly ash bricks. Burning coal in power plants produces fine, powdery fly ash. It is collected by electrostatic precipitators and other pollution control devices before escaping into the atmosphere. Fly ash is a waste material that can be tapped as a valuable resource for producing bricks. Using fly ash in brickmaking can reduce the environmental impact of coal-fired power plants and conserve natural resources like clay, traditionally used in brickmaking.